The world’s direct selling industry is now undergoing a crux moment. Although the overall sales declined 2.3% to $167.6 billion in 2023, this top-line figure conceals breath-taking variations in regions and developing opportunities. Results of data-driven assessment show that some geographic areas (especially in Southeast Asia, Latin America and some parts of Eastern Europe) exhibit strong growth in spite of the worldwide headwinds. This study reveals where the $167 billion direct selling market is really growing, how to find the major growth drivers, and how to see strategic developments of leaders in the market.
Key findings
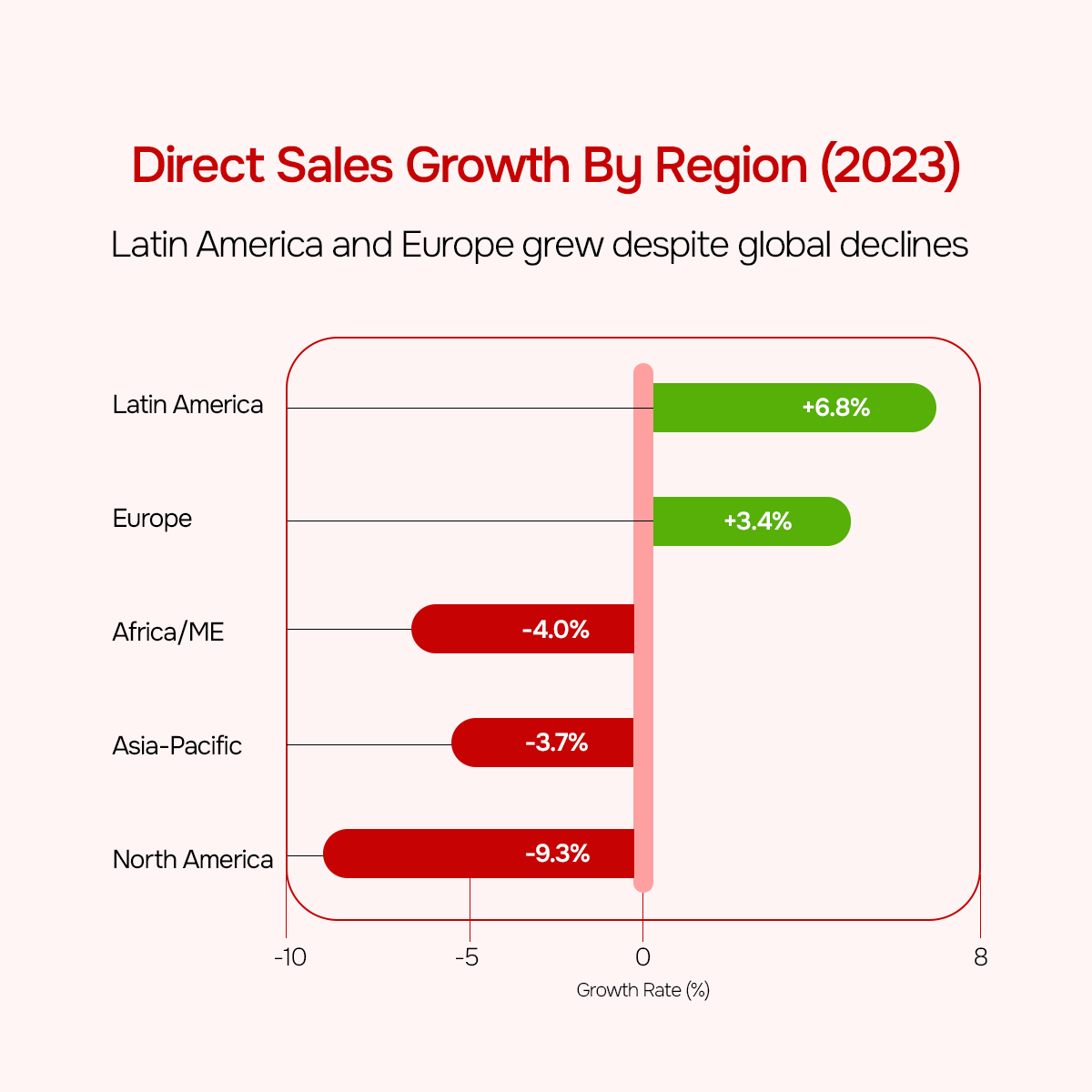
Regional divergence: Latin America and Europe experienced growth of 6.8%, and 3.4% respectively, while North America experienced a decline of 9.3% in 2023.
Digital integration: Social commerce platforms and the mobile-first approach are transforming the productivity of distributors.
Product evolution: Household goods rose to 17% in global sales while wellness and beauty categories dropped by a little bit in share.
Emerging regions: The Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe and certain African markets demonstrate promising growth patterns.
Business model innovation: Hybrid affiliate+MLM models are revamping the industry and turning new players into it.
The current state of global direct selling
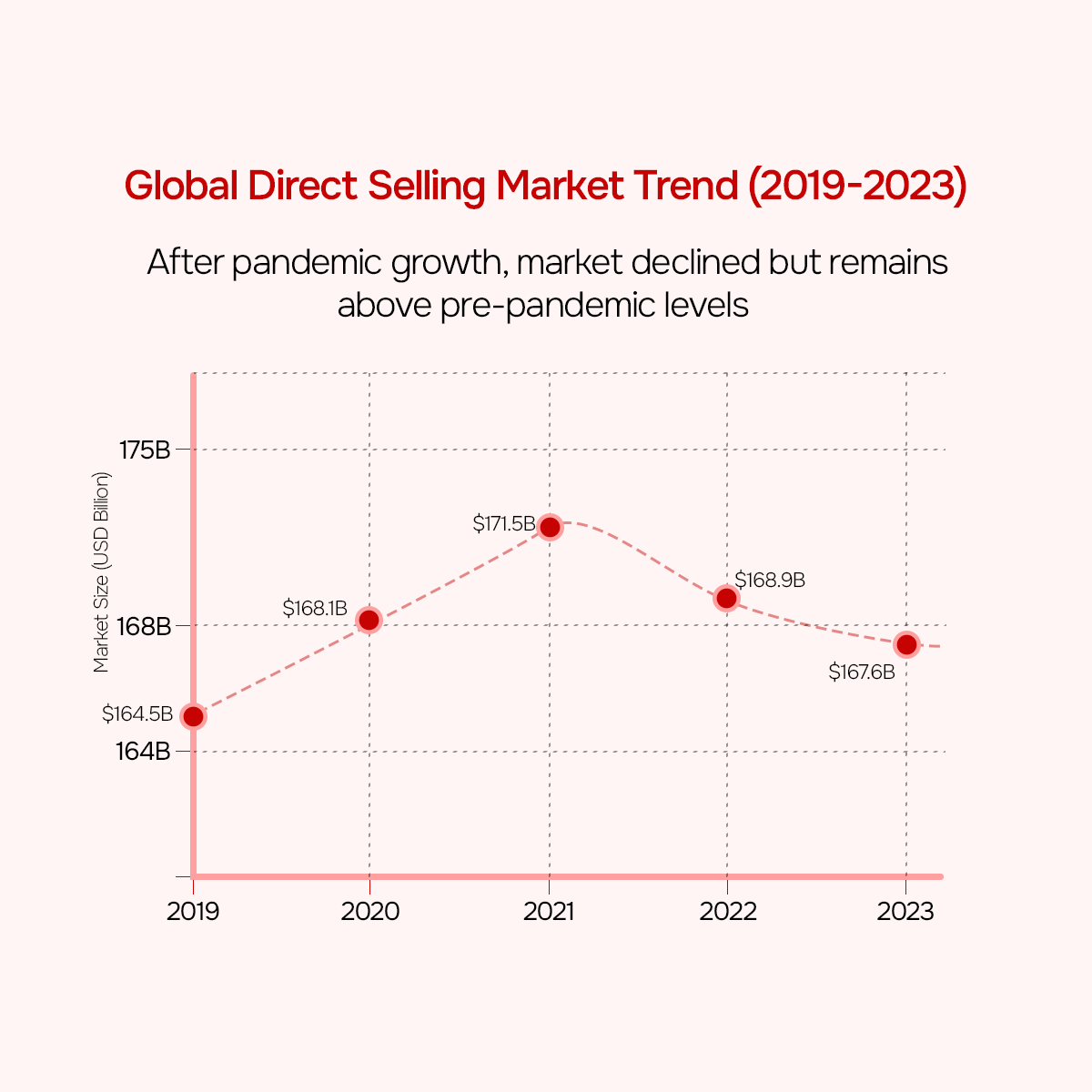
The direct selling industry has been in turmoil in recent years. Having risen after the pandemic in 2020 (+2.2%) and 2021 (+2.0%), the market went down in 2022 (-1.5%) and 2023 (-2.3%). Global direct retail sales reached $167.6 billion in 2023. This is an amount that has remained higher than the pre-pandemic 2019 numbers, proving the fundamental resilience of the direct selling sector.
These global numbers, however, hide significant regional differences. Direct sales across North America fell 9.3% in the year 2023, according to statistics released by the World Federation of Direct Selling Association (WFDSA). On the other hand, Latin America grew by 6.8%, which was the highest growth of any region. At the same time, Europe recorded impressive growth at 3.4%.
But the Asia-Pacific region recorded an overall 3.7% diminution, with most of it being accounted by large East Asian markets. Those of Asia-Pacific, excluding China, actually increased almost 6% to $52.53 billion. Africa and the Middle East, which accounted for only 1% of the world’s direct selling, showed mixed results with a 4.0% decrease overall.
This disparate delivery highlights an industry change, with increasing expansion possibilities for the emerging markets and companies embracing innovative digital strategies.
Regional growth hotspots: Where direct selling is thriving
Southeast Asia: Digital transformation and demographic advantage
Southeast Asia has always been a hotbed for direct sales, although its 2023 results are mixed. The country of Malaysia can be identified as a robust performer, which expands by 1.4% to around $9.5 billion and now belongs to the top direct selling markets of the world. Remarkably, Malaysia is the country with the highest direct selling penetration across the world at 2.3% of GDP, which speaks volumes about the extent of penetration of the channel in the economies of the region.
Digital and demographic tailwinds are driving direct selling business in Southeast Asia. The young, mobile-first population of the region is rapidly adopting social commerce at unimaginable levels. Apps such as TikTok, Facebook, and Instagram are expanding old party plans, allowing vendors to access thousands of customers via live video and short videos.
The development of the micro-fulfillment centers and smarter logistics increases the distributors’ productivity by removing the inventory management and fulfillment flaws. As mobile phone penetration is forecasted to increase to ~94% of all mobile connections by 2030, tens of millions of new consumers and sellers are coming online. This is a huge opportunity for companies that localize their strategy well.
Latin America: Resilient growth through beauty and economic necessity
Latin America had a veritable model of growth in 2023, with sales spiking 6.8% during the year. Besides, millions were joining the field of direct selling, both as consumers who searched for cheap quality products, and as sellers in search of supplemental income in uncertain economic times.
This was a widespread growth across this part of the globe. Brazil, the largest market in the region, and the number one exporter to the region, gained 4.6%, to $8.0 billion; and Mexico picked up 3.0% to $6.87 billion. A number of small markets doubled or even tripled in size. Argentina posted a +114% growth in constant USDs as local population stocked on products and participated in seller programs to hedge against high inflation.
When it comes to direct selling resilience in Latin America, product mix and cultural fit are the keys. Cosmetics represented a stunning 73% of the direct sales in Brazil in 2023, and in South & Central America, cosmetics & personal care represented 59% in direct selling. In fact, this is much more than the world average. Latin consumers have established ties with people from the neighborhood for beauty essentials, wellness capsules, and home products.
The other powerful growth driver is economic necessity entrepreneurship. Considering that many Latin American countries are experiencing inflation and few formal opportunities to earn, direct selling provides a flexible lifeline. Over 13 million people are being employed as independent representatives in South & Central America, and unlike in North America their sales force has been increasing.
Eastern Europe: Surprising bright spots in the middle of challenges
Eastern Europe provided some of the most exciting growth numbers out of any of the regions in 2023. Though overall direct sales in Europe increased moderately (+ 3.4 %), Eastern Europe fueled this increase.
In 2023, the direct selling market of Turkey grew at a phenomenal 81.3% compared to the year before, one of the highest growths in the world. Sales in war-ravaged Ukraine also went up by an impressive 35.7% amidst the obstacles. A number of Eastern EU countries also displayed healthy gains: Bulgaria grew 29.1% and Slovenia 6.4%. By contrast, the largest market in Western Europe such as France (0,0%), Italy (-0.3%) and the UK (-10%) stood still or declined.
Culturally, Eastern Europe has adopted wellness and services categories that are gaining heat in the world. In contrast to Latin America’s beauty focus, many Eastern European consumers are inclined to wellness products and even financial or useful services that are being offered through network marketing.
Product category shifts: Evolving consumer preferences
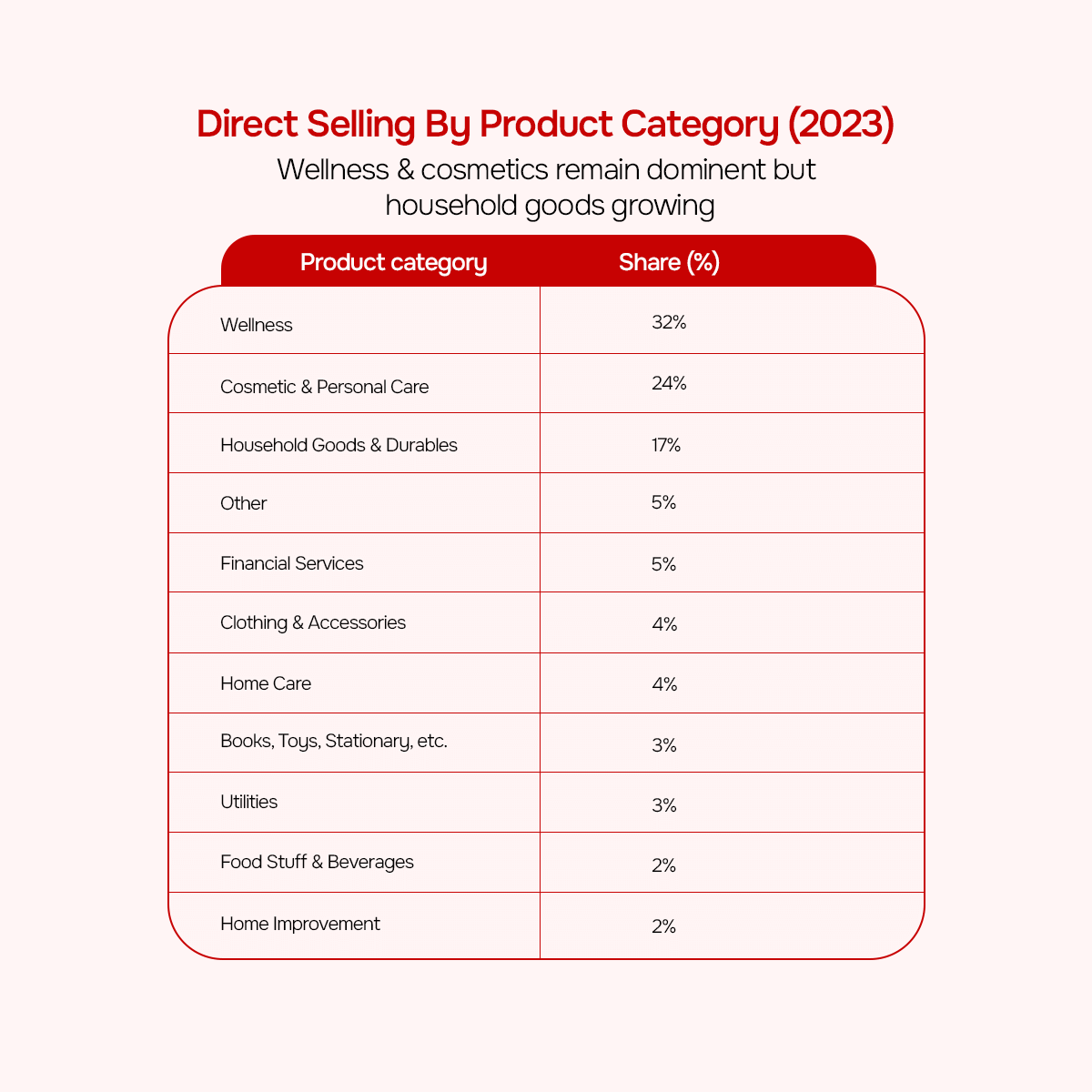
Direct selling has undergone a lot of changes with regards to product mix in recent years. There are three categories that rule the world’s direct sales from 2023.
Wellness products (decline from 36% to 32% in sales).
Cosmetics & personal care (24% of sales, decline from 27% in 2019).
Household goods & durables (17% of sales, up from 12% in 2019).
Combined, these three spheres accounted for 73% of the overall revenue produced from direct selling.
The minimal drop seen on the wellness share reflects normalization out of a pandemic boom. In 2020-2021, the consumers of the world stocked up on vitamins, immunity boosters, and weight-loss products via the MLM circuit. With the pandemic cooling down, people began to purchase again from pharmacies and stores. Thus, the direct selling wellness sales in some areas levelled off. However, the dominance of wellness is still there, particularly in Asia Pacific, where it is ruling 39% of the regional direct sales.
Beauty and personal care also lost a bit of ground, probably because of the explosion of indie brands and sales based on influencers, outside of MLM. Nonetheless, beauty remains the #2 category worldwide as well as totally dominant in such areas as Latin America (59% share).
The increase in the household goods durables category by 17% is one of the greatest trends. This would encompass long-lasting home products, which are regularly presented in person, high-end kitchen items, home appliances, air purifiers, and storage solutions. Due to the pandemic, there was a nesting trend whereby people used to invest in their home environments and direct sellers took advantage of such a change.
Outside the top three, a number of niche categories are taking off.
Financial services (5% of global sales): Insurance policies, investment programs, subscriptions for legal aid services.
Home care (4%): Cleaning products, laundry detergents.
Clothing & accessories (4%): Fashion, jewelry.
Utilities (3%): Products offered by electricity, gas or phone services resold by MLM.
Other (5%): Travel packages, health services, and newer concepts.
Why some markets are expanding despite global headwinds
A number of cross cutting themes emerge from our examination of high-growth regions and categories:
1. Social commerce and digital integration driving productivity
Markets that adopted social selling tools early on have outperformed their peers. Increasing trends of TikTok commerce, WhatsApp selling groups, and distributor-driven ecommerce have hugely expanded the reach of direct sellers. This trend increases distributor productivity at the individual level; one person can now sell to hundreds of customers through the internet instead of a few in person.
Micro-fulfillment infrastructure as a response to this digital shift helps to guarantee a rapid fulfilment of online orders. A seller in Manila or Lagos can receive an order on Facebook Live and have the product delivered from a local micro-warehouse the next day without ever touching inventory. This is truly a game-changer for scale in sales.
2. Economic need and entrepreneurial culture
Direct selling thrives where employment or retail is poor and where the spirit of entrepreneurship is strong. The Latin American case reflects this dynamic, where high unemployment or inflation drove people to find income in direct selling.
The same is true for Eastern Europe’s growth and Africa’s growth, which represents communities literally grabbing economic fate in their own hands through micro-entrepreneurship. The global dip of 2023 was mostly a phenomenon of the developed markets. Markets were developing, basically because the motors (need for income, need for convenient goods) were strong.
3. Shifts in product demand
Regions with a higher rate of growth usually had the ideal blend of products for the existing attitude of the consumers. People in an inflationary environment tend to look for value and durability. As a result, durable home goods did well as an investment and Latin American’s value-for-money cosmetics sold very well. Heightened concern for health and wellness continued post-pandemic, contributing to major wellness based MLM markets such as India and Malaysia.
4. Hybrid sales models - New sellers’ attraction
The hybrid affiliate+MLM models are coming up and increasing sales, since it attracts those who may not join a traditional MLM. When the companies simplify their compensation plan to emphasize on sales commissions instead of recruitment incentives, they send a clear signal that attracts influencers, or casual sellers interested in referral income but do not want to build a down line.
These affiliates usually have a huge fan-base; they can create an enormous volume without recruits. The outcome may be higher average revenue per distributor (fewer people in distribution positions, but with each selling a lot more to a larger base of people). This model also has fewer regulatory issues to deal with and can be able to cross borders to marketplaces, in which modern MLM may find opposition.
5. Improved infrastructure and ecosystem support
In countries where direct selling is developing, off the scene infrastructure has frequently been enhanced. Several Direct Selling Associations in the emerging markets have collaborated with governments to unscramble legal status and abolish pyramid schemes, which has increased the confidence of consumers. Logistics improvements and improvements in payment systems (such as mobile money in Africa) allow distributors to collect payments and get commissions even in places where there is no traditional banking.
New commission management tools that support multi-currency payouts and enable incorporating local compliance checks also make international transactions easy. As a result, companies can take advantage of diaspora networks and social reach crossing borders.
Discover how we build resilient businesses with advanced MLM functionalities
Strategic implications for industry leaders
There are a number of strategic imperatives for the executives and entrepreneurs in direct selling:
1. Give precedence to growing regions while approaching locally
Companies that are stuck in plateaued growth should look at emerging markets such as South East Asia, South Asia, Latin America, and developing pockets across Eastern Europe and Africa. This is not just about finding the distributors, but it is about making your approach truly local.
Make sure that systems have the capability to account for localized tax logic (VAT in Europe, GST in India, fluctuating sales taxes throughout Latin America) to ensure they stay compliant. Offer marketing materials and back-office portals in local languages. Demonstrate culture sensitivity through localization of product offerings, more skin-brightening in Asia if popular, more weight management in places where that’s glaringly needed.
2. Integrate social selling tools and platforms
The distributors of today are both creators of content and community builders. Companies should adopt an integration with social platforms whenever possible, linking up product catalogs and commission logging with TikTok Shop or Facebook Shops. This means that when the distributors do sales through livestreams and referral links, transactions are reflected uninterruptedly in their dashboards and payouts smoothly.
Offer shareable content libraries as part of distributor apps in order to facilitate high-quality product showcases with a minimum effort. Install affiliate tracking facilities for online shopping to enable the distributors to get credit for digital sales, synergizing the potential of channel battle.
3. Have smart commission routing and flexible payout systems in place
Cross-border and digital sales create complex compensation scenarios, which can be leveraged as competitive advantages once the right systems are in place. The commission engines should have a multi-currency feature and instant payouts. If one of the distributors in Kenya sells to someone in Germany through a personal website, the system should automatically convert euro sale into local currency earnings, tax concerns if any and credit there e-wallet, ideally in real time.
Smart commission routing also involves handling genealogies over borders through way of mapping distributors to country or currency and overrides calculated accordingly. This eases friction in international expansion as well as the organic growth of distributor networks on a global scale.
4. Implement mobile first design for both distributors and customers
In a highly competitive and digital world, mobile-first design is important for distributor tools and customer interfaces alike. MLM apps should allow distributors to undertake any function on the mobile devices: register prospects, order, track delivery, get access to training, track commissions, and share product links.
Equip field teams with practical data visuals on mobile dashboards, which product is moving best, commission forecasts and status to bonus tier statuses. Most of the growth markets—India, Africa, Southeast Asia—are mobile-only or mobile-primary markets, making this approach fundamental for gaining a market share.
5. Enhance compliance and transparency
As the regulatory gaze intensifies internationally, businesses will have to make compliance a part of their operations. This comprises of income disclosures, product claims surveillance, and anti-pyramid protections. Possible practical implementations could include required fields for distributors to record retail sales customers, approval mechanisms for the materials in marketing, and mechanisms for detecting unusual behavioral patterns.
Not only do strong compliance management strategies keep companies out of hot water legally, but they establish a culture of trust. In markets such as the US, being ahead on compliance might turn out to be a competitive edge in future as regulatory frameworks develop.
Future outlook
Hereafter, our research reveals the following trends in the direct selling environment:
Global sales trajectory: Following the two soft years, the world direct selling revenue is set to show a resurgence in moderate growth in 2025 onward, even hitting between $175–180 billion by 2027 (implying a 2–4% CAGR).
Regional leaders: The subregions likely to register the fastest growth are Southeast Asia and South Asia. India may be able to double its direct sales from $3.4 billion to $6 billion in 2027 if it maintains its current double-digit growth. Eastern Europe will be dependent on macroeconomic stability, while Latin America should move forward with mid-single-digit growth.
Product category evolution: Wellness might gain traction due to the aging world population and wellness technology trends. Beauty and personal care may be enhanced by AR/VR innovations and influencer strategies. There is a possibility that the household durables will continue to be strong with possible growth in the field of smart homes and sustainable solutions.
Distributor models: The worldwide sales force could level at 100 million where the serious sellers can make up a greater share than the casual participants. Average revenue per distributor is likely to further increase with the companies targeting productive business builders and digital tools to increase the efficiency running of the business.
Technology integration: By 2025, almost all of the competitive direct selling companies will have mobile first systems with AI-powered recommendations, real-time inventory visibility, and CRM-like features. VR demonstrations of products and immediate payments of commission, as well as tools for transparency based on the blockchain, can become the standard in the industry.
Conclusion
The world of direct selling is not shrinking, in fact, it’s expanding. New areas, categories of products, and approaches to selling are becoming popular for the $167 billion market. The southeast Asian and Latin American communities are adding new vigor to the channel, whereas North America and the West are rethinking their strategies.
The growth of social commerce and digital micro-entrepreneurship allows direct selling to cover previously unreachable masses of consumers. The figures suggest healthy diversification by product categories, which indicates an improvement in tolerance to market sections.
For the leaders in industries, the call is obvious: drive this transformation instead of being driven by it. Use data-driven insights to make strategy, be ready to pivot when needed, and never forget about the human factor in direct sales that makes it special. Successful companies will be those that narrow the gap between the technological revolution and the personal touch that the direct selling business has always been based on.
Sources
World Federation of Direct Selling Associations (WFDSA) – 2024 Statistical Report Highlights
WFDSA Global Sales Data (2023) – Regional and Country Breakdown
Direct Selling News – WFDSA Releases 2024 Global Statistical Data (Sept 2024)
World of Direct Selling – Global Direct Selling 2023 Review (H. Ozmorali)
WFDSA Product Category Breakdown (2023)
WFDSA Top Markets and Penetration Data
Direct Selling News – Monat Launches TikTok Shop (Mar 2025)
GSMA – The Mobile Economy 2023 (smartphone adoption stats)








Leave your comment
Fill up and remark your valuable comment.